[Answered] Do Carbon Resistors Go Bad?
Yes, carbon resistors can go bad over time. The lifespan of a carbon resistor, like any electronic component, depends on various factors, including its quality, operating conditions, and usage patterns.

What Is Carbon Resistor
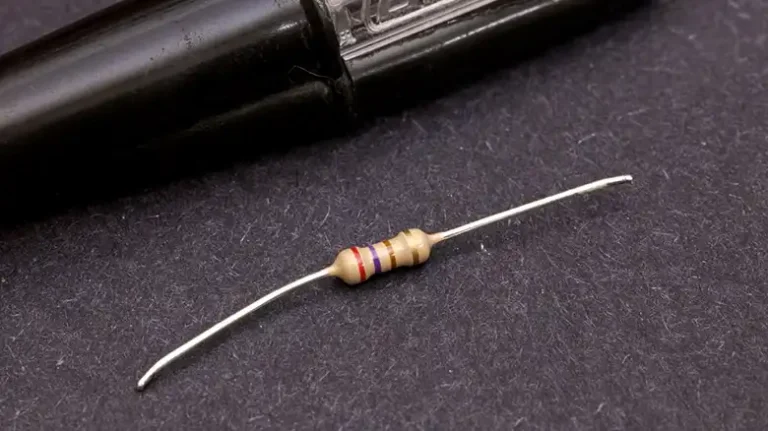
A carbon resistor is a type of fixed-value resistor that is formed of a binding substance, usually ceramic, and a mixture of carbon particles that are molded into a cylindrical or rectangular shape.

Figure: Carbon Resistors.
The electrical resistance of a carbon resistor depends on the composition and physical dimensions of the resistor. The electrical resistance (R) of a carbon resistor is given by Ohm’s Law:
R = V / I
where:
R = Resistance (measured in ohms, Ω)
V = Voltage across the resistor (measured in volts, V)
I = Current flowing through the resistor (measured in amperes, A)
Carbon Resistor Mechanism
A carbon resistor works by opposing the flow of electric current through the resistance provided by the carbon composition. When a voltage is applied across the resistor, the flow of electrons encounters resistance as they interact with the carbon particles within the resistor.
Carbon, being a resistive material, hinders the movement of electrons. This resistance to the flow of current is what causes the voltage drop across the resistor and limits the amount of current passing through it.
Carbon Composition Pulse Power Capability
Long rods of carbon and ceramic binder material are used to create the carbon composite resistive element. In order to attain the requisite resistance value, the elements are then cut from the rods at the appropriate length. Then leads are placed into the ends of the material and the units are fired to cure them.
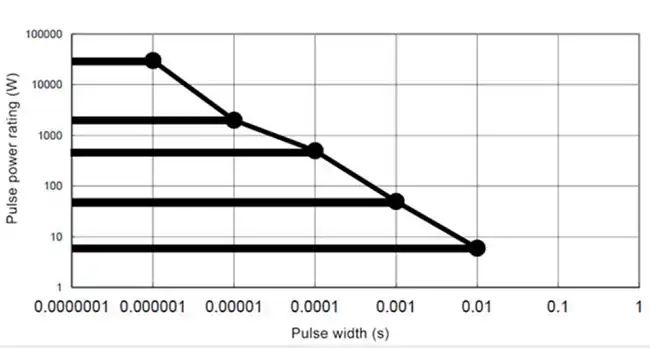
Figure: Carbon Composition Pulse Power Capability
What Makes Carbon Resistors Go Bad
Several factors are reasonable for carbon resistors to go bad. Here are some reasons that can turn a carbon resistor bad:
- Overheating: If a carbon resistor is subjected to excessive power dissipation beyond its rated wattage, it can overheat and potentially fail. High temperatures can cause the carbon composition to deteriorate faster, leading to a shift in resistance value or even an open circuit.
- Ageing: Over time, the carbon composition of the resistor can degrade, leading to changes in its resistance value. This ageing process can be accelerated if the resistor is operated at high temperatures, near its power rating, or in harsh environments.
- Mechanical Stress: Physical stress or mechanical shock can damage the carbon resistor’s structure, affecting its electrical properties and leading to failure.
- Moisture and Contaminants: Carbon resistors are sensitive to moisture and contaminants. Exposure to high humidity or corrosive substances can cause the resistance value to change or create intermittent connections.
Can Resistors Change Value Over Time
Yes, resistors can change value over time due to various factors. This change is often referred to as resistor drift or ageing. The extent of drift depends on the resistor’s construction, material, and environmental conditions to which it is exposed.
Ageing, temperature variations, contaminations, and high power dissipation are the factors that can cause resistors to change value over time.
How Long Do Carbon Resistors Last
Generally, carbon resistors are designed to be reliable and have reasonably long lifespans when used within their specifications. Operating conditions, quality, environment, and power dissipation are the factors that can influence the lifespan of a resistor.
If operated well below their maximum power rating and within their specified temperature range, carbon resistors can last for thousands of hours or even longer.
How To Prevent Carbon Resistors From Being Bad
To prevent carbon resistors from failing prematurely or becoming unreliable, these guidelines should be followed:
- Always use carbon resistors within their rated power and temperature limits. Avoid exceeding the maximum power rating to prevent overheating and potential failure.
- Keep carbon resistors away from moisture, dust, and corrosive substances. Enclose or protect them in a suitable enclosure if necessary, especially in harsh environments.
- Protect the resistor from voltage spikes or transients that can lead to excessive stress on the resistor and cause damage.
- If the resistor generates heat during operation, ensure proper heat dissipation to prevent thermal stress.
- If you anticipate high ambient temperatures or expect variations in operating conditions, consider derating the power handling capability of the resistor. Running the resistor at lower power levels can extend its lifespan.
How Do I Know If My Resistor Is Bad?
Circuit malfunction or erratic behavior and open circuit (no current flow) or short circuit (excessive current flow) will be observed. Sometimes a burning smell from the resistor will also be observed. These are the signs of a bad resistor.
Conclusion
Carbon resistors are commonly used in voltage dividers, current limiters, and signal conditioning circuits. In critical or precision applications, alternative resistor types may be preferred to minimize the risk of resistor failure and ensure better long-term performance.